"navigating the Sound Spectrum: What is Frequency Response in Headphones"
Introduction
In the age of booming technology, headphones are no longer just about listening to music. They've evolved into an essential tool for creating immersive audio experiences, from intense gaming to audio editing and enjoying high-definition movies. One aspect that profoundly influences the performance of these headphones is the 'Frequency Response'. This blog will delve into what frequency response in headphones means, its significance, and how to use this knowledge to amp up your listening experience.
What is Frequency Response and Why is it Significant?
Deconstructing the Physics of Frequency
Frequency response in headphones defines the range of frequencies that they can reproduce effectively. It's typically depicted within a scope, say 20Hz-20kHz, essentially mirroring the human auditory spectrum. Expansive frequency ranges suggest headphones with the versatility to produce an array of sound frequencies, contributing to a more robust and diverse auditory experience.
Here's a quick physics rundown to better grasp the concept:
- High Frequencies: These correlate to high-pitched sounds such as those produced by a flute.
- Low Frequencies: These resonate with deep bass sounds like a drum beat.
Therefore, the frequency response of your headphones can make or break your ability to perceive these high and lows optimally.
The Influence of Frequency Response on Sound Quality in Headphones
The prominence of frequency response lies in its power to shape the sound you hear. When specific frequencies are either amplified or subdued, it distorts the overall sound rendering, possibly leading to an unsatisfactory listening session. Headphones with a balanced frequency response allow audio to be perceived exactly how the artist intended it to be, providing an authentic and pleasing experience.
Key takeaway:
- Distorted Frequencies: Elevated or suppressed frequencies alter the sound and may lead to a subpar listening experience.
- Balanced Frequency Response: A well-balanced frequency response allows the authentic and intended reproduction of the audio track.
Realizing the full potential of your headphones entails understanding the concept of frequency response - not just what it is, but how it factors into the sounds that reach your ears. Whether you're an audiophile seeking high-fidelity sound reproduction or a casual listener who values quality, frequency response should form a critical part of your headphone selection criteria.
What Role Does Frequency Response Play in Different Types of Headphones?
As the diversity in our audio needs escalates, so does the demand for varying types of headphones tailored to meet these needs. The choice of headphones for a comfortable evening jog may differ significantly from a pair you'd reach for to relish the recordings of a newly released symphony or a live concert. Here, we dive into how frequency response plays its part in distinct kinds of headphones, particularly focusing on the most common varieties – Over-ear and In-ear headphones.
Over-Ear vs. In-Ear Headphones – A Frequency Response Faceoff
Due to their divergent designs, over-ear and in-ear headphones inherently produce different sound output and frequency responses.
- Over-ear headphones come equipped with larger drivers that provide a wider frequency response. That translates into a more detailed and rich sound experience for the user. They particularly excel in reproducing deep bass sounds, thanks to the more extended lower limit of their frequency response.
- On the other side of the spectrum, in-ear headphones typically shine with high-frequency sounds due to their smaller drivers. This aspect results in highlighting the finer constituents of the audio spectrum such as the vocals, violin strings, flutes, etc.
Selecting Headphones Based on Frequency Response
Different listeners fancy different sound profiles. For instance, a bass enthusiast might prefer headphones with a powerful response in the lower frequencies. On the other hand, someone fond of instrumental music might lean towards headphones that beautifully mirror the audio frequencies' higher end. Your preferred genre can significantly dictate your headphone choice based on its frequency response.
Here are some consideration points:
- Identify your audio needs: Are you a professional music artist requiring a balanced sound? Or a podcast enthusiast, where vocals matter the most?
- Know your preferred sounds: Do you enjoy deep bass, or are you more of a high-frequency fanatic?
- Cross-check with headphone specifications: Once you have recognized your needs, check the headphone frequency response specifications to ensure they're suited to your preferences.
In this manner, understanding the frequency response paves the way for an informed choice, letting us marry our audio needs with the most compatible headphones.
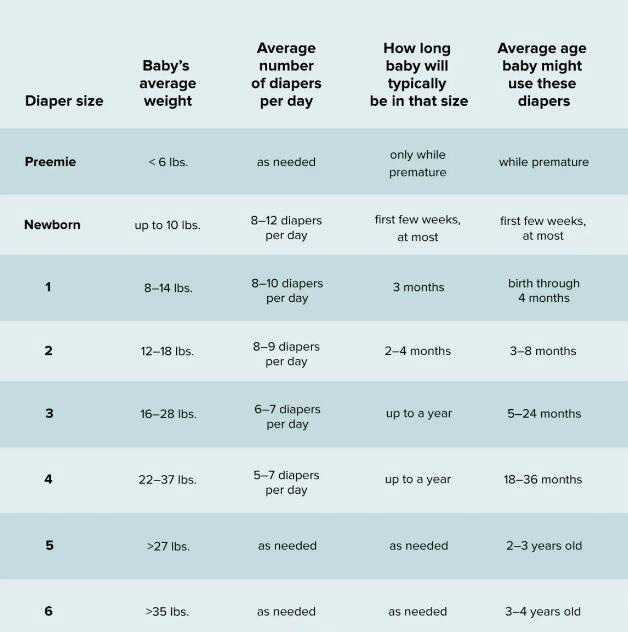
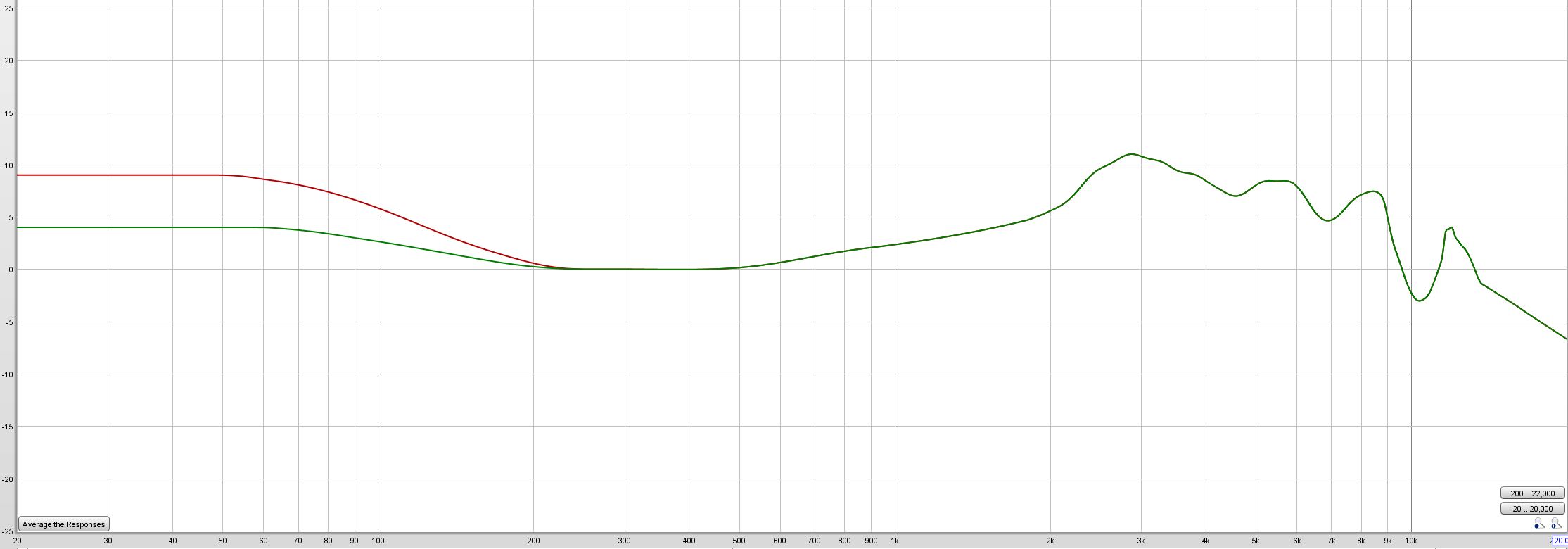
How to Read and Interpret Frequency Response Charts?
Mastering the Art of Frequency Graphs
Interpreting frequency response charts might seem overwhelming at first glance. However, they are relatively straightforward once you understand the fundamentals:
- Each graph's x-axis represents the frequency range, generally extending from 20Hz at the low end (bass sounds) to 20,000Hz (20 kHz) at the high end (treble sounds). This range emulates the average range of human hearing.
- The graph's y-axis signifies the dB level (decibel level), displaying how loudly the headphones play each frequency. A higher dB level indicates that a particular frequency plays louder when compared to frequencies with lower levels.
- An ideally flat line on the graph means the headphones reproduce all frequencies at the same volume, ensuring uncolored and accurate sound reproduction.
Influences on Sound Quality
The frequency response on these charts significantly impacts the sound quality in the following ways:
- Prominent Bass: If the graph shows a boost in the low-frequency range (20Hz - 200Hz), it indicates that headphones will produce pronounced bass sounds. This fulsome bass can create a warm sound environment favoring genres like hip-hop, EDM, and more.
- Enhanced High-End: A boost in the high-frequency range (2kHz - 20kHz) means the headphones will emphasize 'bright' sounds like a tambourine's sizzle or a singer's sibilance. These headphones could be optimal for genres focusing on vocals and high-frequency instruments.
- V-shaped response: If the graph shows a boost in both low and high frequencies with a dip in the middle, it represents a V-shaped (or U-shaped) response. Such headphones can make the music exciting to listen to, though they might not be ideal for listeners seeking neutral or uncoloured sound representation.
By learning to read and comprehend these frequency response charts, one can tailor their audio experience according to personal preferences, making your listening journey a truly personalized experience.
Can Understanding Frequency Response Improve the Listening Experience?
Personalizing Your Sonic Landscape
Recognizing the intricacies of frequency response can be transformative for personalizing your audio atmosphere. The magic lies in grasping the fact that different sound frequencies interact with your ear differently, and every headphone is inherently designed to emphasize certain frequencies over others, shaping our individual aural experiences.
Does your music taste lean towards bass-heavy tracks? Or do you relish the high-pitched sounds of violins? Understanding frequency response allows you to tailor your headphones' choice to your music preference, ensuring that you relish every note the way it's meant to be heard.
Pointers for Musicians, Audiophiles, and Regular Users
The importance of grasping the concept of frequency response magnifies for certain groups like musicians and audiophiles, along with everyday users. Here are some crucial points to consider:
- Musicians: A balanced, natural-sounding frequency response is typically preferred to avoid colouring the sound produced. This allows musicians to be true to their creativity, hearing the strum of every string, the beat of every drum the way it was intended.
- Audiophiles: The key lies in achieving the sound closest to the original recording. They often lean towards headphones with a wide frequency response range for a richer, more detailed sound.
- Everyday Users: For day-to-day music listeners who may not have a particular genre preference or focus on explicit details, an understanding of frequency response can still significantly enhance their listening journey. The balance emphasizes personal preference – if you like more bass, look for a higher amplitude in the lower frequencies (20Hz – 200Hz). Conversely, if vocals and high notes are your thing, the focus should be on the higher frequencies (2kHz to 20kHz).
Thus, understanding frequency response can significantly enhance the listening experience by ensuring the headphones you choose align well with your unique aural preferences. This intuitive understanding can potentially help you comprehend and appreciate music better, making for a more immersive, engaging, and gratifying listening experience.
Conclusion
Over-ear headphones, with their larger drivers, have a more comprehensive frequency response, offering a richer, more immersive sound experience. In contrast, in-ear headphones, with their smaller drivers, typically emphasize higher frequencies, making them great for listening to vocals and instruments like violins. However, over-ear models may be more comfortable for long periods, a factor worth considering alongside frequency response.
Related FAQs about what is frequency response in headphones
What is the human hearing range and how does it relate to headphone frequency response?
The average human hearing range extends from 20Hz to 20kHz. This range is considered for designing headphone frequency responses. Ideally, headphones should cover this scope, ensuring the accurate reproduction of bass (low frequencies) to treble (high frequencies) for an optimum listening experience.
How does frequency response affect the quality of sound in headphones?
Frequency response dictates how each frequency is played, from low (bass) to high (treble). Balanced response offers authentic reproduction, while amplified or suppressed frequencies may distort sound. Headphone style, including over-ear or in-ear, also impacts frequency response, thereby affecting sound quality.
What is the ideal frequency response for listening to music, watching movies, and gaming?
It depends on personal preference. For bass-heavy music and action-filled movies or games, headphones with enhanced lower frequencies (bass) may be ideal. For vocal-driven music or dialogue-heavy films, headphones accentuating higher frequencies (treble) may be better. A balanced response suits most genres and use-cases.