Getting Familiar With Your Computer: What Does a Hard Drive Look Like?
Introduction
In an era of ever-increasing digital dependence, understanding the basics of your computer hardware is essential. One of the crucial components of any computer is the hard drive. But what does the hard drive of a computer look like, and why does it matter? This guide will help you understand the appearance, structure, and function of computer hard drives, looking at different types like HDD and SSD, and explaining how they've evolved over time.
What is a Computer Hard Drive?
A computer hard drive, often shortened to HDD (Hard Disk Drive), plays a critical role as the main storage unit in your computer or laptop. All data, including the operating system, applications, files, and folders, are stored here.
- What does it look like? Typically, an HDD is a rectangular metallic box inside the computer's system unit. In laptops, they're usually tucked away at the side or bottom, under a small cover that can be removed.
- Types of hard drives: There are two major types of hard drives – the standard HDD and the increasingly popular SSD (Solid State Drive). SSDs are renowned for their speed and efficiency, making them a preferred choice for many users.
- Positions by type: While HDDs are often found in the system unit of desktops or the side/bottom of laptops, SSDs can be located in different places due to their variable sizes and shapes.
Remember, the type of hard drive you use can significantly impact your computer's performance and speed. Many are shifting towards SSD due to its advanced features and advantages over traditional HDDs.
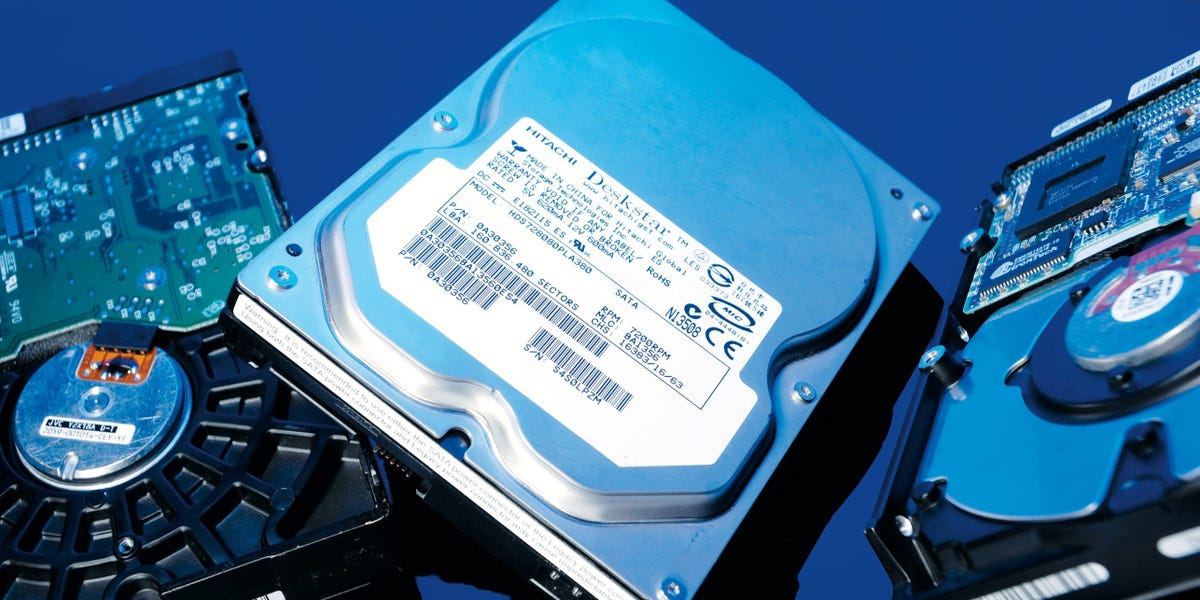

A Detailed Description of a Hard Drive: How to Recognize It?
A hard drive is typically easy to recognize. Traditionally, hard disk drives (HDDs) are fashioned into box-like, rectangular structures that can be found in desktop computers. Laptop hard drives can be located on the side or the bottom, covered by a removable panel. Here's a thorough breakdown to help you identify different types of hard drives:
Traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDD):
- Shape & Size: HDDs typically come in a rectangular, metallic box format. Desktop versions often measure 3.5 inches in width, while laptop versions are usually 2.5 inches wide.
- Connectors: It features connectors indicating where to link it with the motherboard. SATA connectors for newer drives and IDE for older versions are often present.
- Markings: Look for a label on top of most drives displaying the brand name and the storage capacity.
Solid State Drives (SSD):
SSDs are becoming increasingly popular due to their superior speed and efficiency. But recognizing them can be a bit tricky as they come in various shapes and sizes.
- Shape & Size: SSDs may resemble traditional HDDs but are generally thinner, lighter, and smaller. There are also M.2 SSDs which resemble a stick of gum and card-like PCIe SSDs, perfectly designed for high-performance computers.
- Connectors: Like HDDs, SSDs have connectors indicating where it joins with the motherboard.
- Markings: Similar to HDDs, SSDs feature a label that portrays the brand name and storage capacity.
Once you understand the principal visual cues, identifying a hard drive becomes a straightforward task. It takes just a little familiarity and awareness and you'll be able to discern the SSDs from the HDDs, appreciate their role in your computer's operation and performance, and even make more informed decisions when considering upgrades or repairs.
The Inside of a Hard Drive: What Makes It Work?
The intricate functions of a computer's hard drive rest on its internal attributes. The hard drive's operation hinges on several key components, each with a unique role. In terms of structure and functionality, there's a pronounced difference between the Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and Solid State Drives (SSD).
The Anatomy of a Hard Disk Drive (HDD):
- Spinning Platters: The HDD basis of operations are its spinning platters coated in magnetic material. These disks' purpose is to store the data in digital format.
- Read/Write Head: The read/write head intervenes next by traversing the platters as they spin. Its role is to retrieve or record the data from the platters.
- Motor: The motor plays a dual role in the HDD—it makes the platters spin and manoeuvres the heads.
In terms of operation, an HDD is analogous to a record player where the data is saved on the spinning disk through magnetic polarities.
The Structure of a Solid State Drive (SSD):
SSD operates quite differently from the HDD. Key components include:
- Embedded Processor: Otherwise known as the 'controller,' this processor mediates the operations of reading and writing data.
- Flash-memory Chips: Data in SSDs are stored in these mutually connected flash-memory chips.
Unlike an HDD, SSDs lack moving parts, thereby making it a more durable choice for storage. As the technology advances, SSDs are becoming more popular due to their efficient operation and resilience.
HDD Vs. SSD: How to Distinguish Them?
While hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) may serve the same fundamental purpose - to store and retrieve digital information, they vary significantly in terms of form, functioning, and efficiency. To distinguish between the two, here are the specific characteristics one can consider:
Physical Appearance
- HDD Appearance: HDDs typically appear as rectangular, metallic boxes. For desktops, they are often 3.5 inches wide, while those designed for laptops measure about 2.5 inches.
- SSD Appearance: SSDs are diversified in terms of their physical form. Traditional SSDs mimic the rectangular shape of HDDs but are generally thinner and lighter. However, new-age SSDs like M.2 and PCIe SSDs bear resemblance to a stick or a card, respectively.
Functional Features
When we compare the functional attributes of both data storage devices, one can notice a significant performance difference:
- HDD Functioning: HDDs rely on traditional mechanical means to store data. They operate through spinning platters, overseen by a moving read/write head. As a result, they tend to generate noise when in operation.
- SSD Functioning: Contrary to HDDs, SSDs operate without any moving parts, making them quieter. SSDs use a processor ('controller') for data reading and writing tasks, while data storage happens in interconnected flash-memory chips.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each type of drive offers its unique set of benefits and trade-offs:

- HDD Pros and Cons: HDDs are known for their affordability in terms of cost per unit of storage. However, they consume more power and perform slower data transfers compared to SSDs.
- SSD Pros and Cons: SSDs outdo HDDs in terms of speed, durability, and power efficiency. Nevertheless, they typically cost more per GB of storage.
The Verdict
To sum it up, distinguishing HDDs from SSDs involves evaluating their physical features and operational capabilities. HDDs are your go-to for budget-friendly storage options, while SSDs deliver superior performance, albeit at a higher cost. Being aware of these differences is key in making an informed decision when purchasing or upgrading a computer system.
The Evolution of Hard Drives: How Have They Changed in Appearance?
The look and design of hard drives have undeniably undergone remarkable changes since their earliest form. This has made them more compact and efficient, adequately supporting the demands of modern computing tasks. Here's a snapshot of this evolutionary journey:
1. Size and Data Capacity: In their formative years, hard drives were gigantic machines accommodating only a few megabytes of data. This contrasted sharply with today's hard drives, both HDDs and SSDs, which routinely hold terabytes of data despite their significantly diminished size.
2. Physical Structure: Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) have seen a reduction in physical dimensions over the years. They evolved from the once-standard 5.25-inch size down to the now prevalent 3.5-inch for desktops and 2.5-inch for laptops.
3. Advent of SSDs: Solid-State Drives (SSDs) have brought about another revolution in hard drive design. Traditional box-shaped SSDs look somewhat similar to HDDs but are often much thinner and lighter. Still, the truly impressive transformation lies in the development of M.2 SSDs and PCIe SSDs. These variants resemble a stick of gum or a small card, respectively, greatly minimizing space without compromising data storage capacity.
So, the evolution of hard drives doesn't merely reflect the progress of technology; it signifies the continuous adaptation to meet user demands for more storage in limited physical spaces.
Conclusion
Understanding what a hard drive looks like and how it works is crucial in navigating today's tech-reliant world. Whether it’s an HDD or an SSD, recognizing them and understanding their differences not only helps in upgrading or troubleshooting your PC but also aids in making informed choices when purchasing a new system.
Related FAQs about what does the hard drive of a computer look like
Why is it important to know what your hard drive looks like?
Recognizing your hard drive aids in troubleshooting and upgrading your computer system. It helps not only recognize disk failures but also make informed choices about suitable replacements or even supplementary storage if required.
What are the main components inside a hard drive and what are their functions?
In HDDs, the main components are spinning platters for data storage, read/write heads for reading and writing data, and a motor to spin the platters. SSDs utilise an embedded processor for managing data transactions and flash-memory chips for data storage.
What are the key differences between SSDs and HDDs in terms of appearance and function?
SSDs are generally smaller, thinner, and lighter than HDDs. Functionally, SSDs store data in flash-memory chips, making them quieter, faster, more durable, and power-efficient than HDDs which use spinning disks and read/write heads for data transactions.